The central nervous system
(CNS) is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except radially symmetric animals such as sponges and jellyfish. It contains the majority of the nervous system and consists of the brain and the spinal cord. Some classifications also include the retina and the cranial nerves in the CNS. Together with the peripheral nervous system, it has a fundamental role in the control of behavior. The CNS is contained within the dorsal cavity, with the brain in the cranial cavity and the spinal cord in the spinal cavity. Invertebrates, the brain is protected by the skull, while the spinal cord is protected by the vertebrae, and both are enclosed in the meninges.
Poliomyelitis
is a viral disease that can affect nerves and can lead to partial or full paralysis.
Poliomyelitis is a disease caused by infection with the poliovirus. The virus spreads by:
- Direct person-to-person contact
- Contact with infected mucus or phlegm from the nose or mouth
- Contact with infected feces
The virus enters through the mouth and nose, multiplies in the throat and intestinal tract, and then is absorbed and spread through the blood and lymph system. The time from being infected with the virus to developing symptoms of disease (incubation) ranges from 5 - 35 days (average 7 - 14 days).
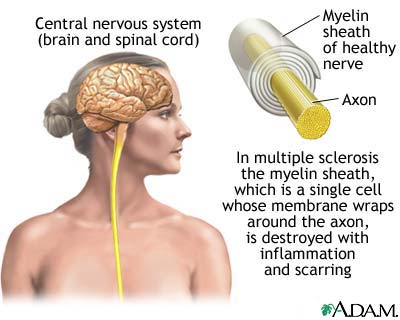
Sclerosis
In medicine, sclerosis (also spelled sclerosus in the names of a few disorders) refers to the stiffening of a structure, usually caused by a replacement of the normal organ-specific tissue with connective tissue.
Types include:
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, sometimes known as Lou Gehrig's disease, a progressive, incurable, usually fatal disease of motor neurons.
- Atherosclerosis, a deposit of fat in the arteries which causes hardening.
- Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis is a disease that attacks the kidney's filtering system (glomeruli) causing serious scarring and thus a cause of nephrotic syndrome in children and adolescents, as well as an important cause of kidney failure in adults
- Hippocampal sclerosis, a brain damage often seen in individuals with temporal lobe epilepsy.
- Lichen sclerosus, a disease hardening and connecting flesh of the vagina of women and the penis of men. An autoimmune disorder.
- Liver sclerosis is a common misspelling of cirrhosis of the liver.
- Multiple sclerosis, or Focal Sclerosis, is a central nervous system disease which affects coordination.
- Osteosclerosis, a condition where the bone density is significantly increased.
- Otosclerosis, a disease of the ears.
- Systemic sclerosis (progressive systemic scleroderma), a rare, chronic disease which affects the skin, and in some cases also blood vessels and internal organs.
- Tuberous sclerosis, a rare genetic disease which affects multiple systems.
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis, a hardening of the bile duct by scarring and repeated inflammation.
- Primary lateral sclerosis, progressive muscle weakness in the voluntary muscles.
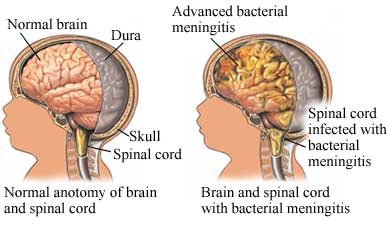
Meningitis
is inflammation of the thin tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord, called the meninges. There are several types of meningitis. The most common is viral meningitis, which you get when a virus enters the body through the nose or mouth and travels to the brain. Bacterial meningitis is rare, but can be deadly. It usually starts with bacteria that cause a cold-like infection. It can block blood vessels in the brain and lead to stroke and brain damage. It can also harm other organs.Pneumococcal infections and meningococcal infections can cause bacterial meningitis.
Anyone can get meningitis, but it is more common in people whose bodies have trouble fighting infections. Meningitis can progress rapidly. You should seek medical care quickly if you have
- A sudden fever
- A severe headache
- A stiff neck
Early treatment can help prevent serious problems, including death. Vaccines can prevent some of the bacterial infections that cause meningitis. Parents of adolescents and students living in college dorms should talk to a doctor about the vaccination.
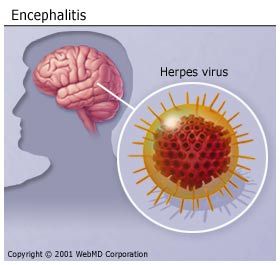
Encephalitis
is an inflammation of the brain. The usual cause is a viral infection, but bacteria can also cause it. Cases can range from mild to severe. For mild cases, you could have flu-like symptoms. Serious cases can cause
- Severe headache
- Sudden fever
- Drowsiness
- Vomiting
- Confusion
- Seizures
For mild cases, you may just need rest, plenty of fluids and a pain reliever. For severe cases, you might need to be hospitalized. Fortunately, encephalitis is uncommon in the United States.
Traumatic brain injury
Traumatic brain injury happens when a bump, blow, jolt, or other head injury causes damage to the brain. Every year, millions of people in the U.S. suffer brain injuries. More than half are bad enough that people must go to the hospital. The worst injuries can lead to permanent brain damage or death.
Half of all traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) are due to motor vehicle accidents. Military personnel are also at risk. Symptoms of a TBI may not appear until days or weeks following the injury. Serious traumatic brain injuries need emergency treatment.
Treatment and outcome depend on the injury. TBI can cause a wide range of changes affecting thinking, sensation, language, or emotions. TBI can be associated with post-traumatic stress disorder. People with severe injuries usually need rehabilitation.
Student With Meningitis




No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario