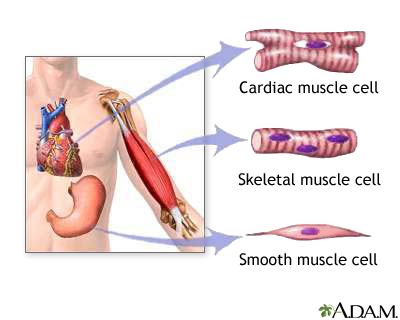
Muscle Tissue
Important!! Muscular System
Muscle atrophy
Muscle atrophy is the wasting or loss of muscle tissue.
There are two types of muscle atrophy.
- Disuse atrophy occurs from a lack of physical activity. In most people, muscle atrophy is caused by not using the muscles enough. People with seated jobs, medical conditions that limit their movement, or decreased activity levels can lose muscle tone and develop atrophy. This type of atrophy can be reversed with exercise and better nutrition. Bedridden people can have significant muscle wasting. Astronauts who are away from the Earth's gravity can develop decreased muscle tone after just a few days of weightlessness.
- The most severe type of muscle atrophy is neurogenic atrophy. It occurs when there is an injury to, or disease of, a nerve that connects to the muscle. This type of muscle atrophy tends to occur more suddenly than disuse atrophy.
Examples of diseases affecting the nerves that control muscles:
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS or Lou Gehrig's disease)
- Guillain-Barre syndrome
- Neuropathy
- Polio (poliomyelitis)
Although people can adapt to muscle atrophy, even minor muscle atrophy usually causes some loss of movement or strength.
Neuromuscular disorders
Neuromuscular disorders affect the nerves that control your voluntary muscles. Voluntary muscles are the ones you can control, like in your arms and legs. Your nerve cells, also called neurons, send the messages that control these muscles. When the neurons become unhealthy or die, communication between your nervous system and muscles breaks down. As a result, your muscles weaken and waste away. The weakness can lead to twitching, cramps, aches and pains, and joint and movement problems. Sometimes it also affects heart function and your ability to breathe.
Examples of neuromuscular disorders include
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Multiple sclerosis
- Muscular dystrophy
- Myasthenia gravis
- Spinal muscular atrophy
Many neuromuscular diseases are genetic, which means they run in families or there is a mutation in your genes. Sometimes, an immune system disorder can cause them. Most of them have no cure. The goal of treatment is to improve symptoms, increase mobility and lengthen life.
Botulism
is a rare but serious illness caused by a bacterium called Clostridium botulinum, which occurs in soil. It produces a toxin that affects your nerves. There are three kinds of botulism. Foodborne botulism comes from eating foods contaminated with the toxin. Wounds infected with toxin-producing bacteria result in wound botulism. Infant botulism is caused by consuming the spores of the bacteria, usually from honey. All three forms can be deadly and are medical emergencies.
Symptoms include double vision, blurred vision, drooping eyelids, slurred speech, difficulty swallowing, dry mouth and muscle weakness. Treatment may include antitoxins, intensive medical care or surgery of infected wounds.
To prevent botulism:
- Be very careful when canning foods at home
- Do not let babies eat honey
- Get prompt medical care for infected wounds
Tetanus
is a serious illness caused by tetanus bacteria. The bacteria live in soil, saliva, dust and manure. The bacteria usually enter the body through a deep cut, like those you might get from cutting yourself with a knife or stepping on a nail.
The infection causes painful tightening of the muscles, usually all over the body. It can lead to "locking" of the jaw, which makes it impossible to open your mouth or swallow. If this happens, you could die of suffocation.
If you get tetanus, there is usually a long course of treatment. The tetanus vaccine can prevent tetanus but its protection does not last forever. Adults should get a tetanus shot, or booster, every 10 years. If you get a bad cut or burn, see your doctor--you may need a booster.
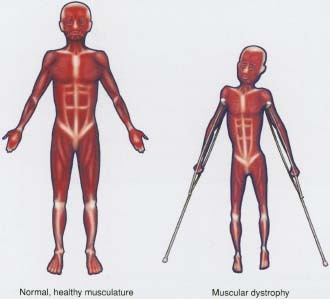
The muscular dystrophies
(MD) are a group of more than 30 genetic diseases characterized by progressive weakness and degeneration of the skeletal muscles that control movement. Some forms of MD are seen in infancy or childhood, while others may not appear until middle age or later. The disorders differ in terms of the distribution and extent of muscle weakness (some forms of MD also affect cardiac muscle), age of onset, rate of progression, and pattern of inheritance.
Professor facing double




No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario